The Root Cause Tree Technique: A Guide to Finding Causal Factors for Better Decisions
- Amara James Moosa

- May 14
- 4 min read
Introduction
The Ishikawa Diagram, or Fishbone Diagram, provides a valuable framework for understanding the potential causes of a problem. However, another powerful tool for root cause analysis is the Root Cause Tree. This article will delve into the intricacies of the Root Cause Tree technique, guiding you through its creation and exploring its diverse applications across various industries. We will cover:
Understanding the Root Cause Tree
A Step-by-Step Guide to Creating a Root Cause Tree
Real-World Application Example
Key Considerations for Effective Root Cause Tree Analysis
Cross-Industry Applications of Root Cause Trees
By the end of this article, you will have a solid understanding of how to leverage the root cause tree to effectively pinpoint root causes and drive data-driven decision-making within your organization.
Understanding the Root Cause Tree
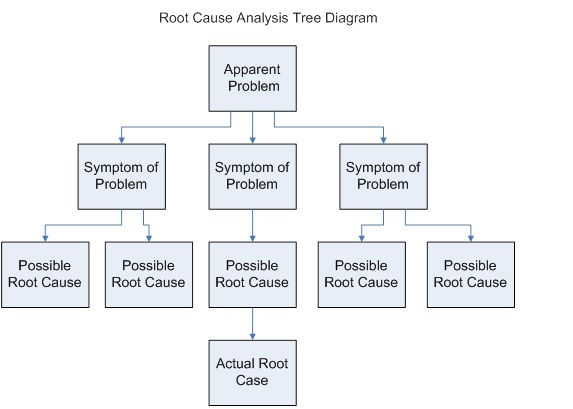
The Root Cause Tree is a visual tool used to identify the underlying causes of a specific problem. It employs a hierarchical structure, resembling an inverted tree, to illustrate the relationships between the problem and its root causes.
Key Components of a Root Cause Tree:
Apparent Problem: The initial, observable problem identified through the situation analysis. This forms the "trunk" of the tree.
Symptoms of the Problem: The observable effects or manifestations of the apparent problem.
Possible Causes: Potential factors that may contribute to the symptoms of the problem.
Actual Causes: The fundamental underlying causes identified through iterative questioning ("Why?") and validated using data analysis techniques (e.g., chi-square tests, correlation analysis).
Visual Representation:
A Step-by-Step Guide to Creating a Root Cause Tree
Crafting a Root Cause Tree: A Step-by-Step Guide
1. Define the Problem and possible causal factors: Clearly and concisely define the problem under investigation.
2. Identify Possible Causal Factors: Determine and list all potential causes or contributing factors related to the defined problem.
3. Build the Tree: Construct the tree structure, starting with the problem as the "trunk" and branching out to identify major contributing factors and their sub-factors.
4. "Why" Analysis: At each level, ask "Why?" repeatedly to uncover deeper causes.
A Real-World Example
Case Study: Sierra Design
Sierra Design, an e-commerce store specializing in graphic design products, is facing a significant challenge: a high cart abandonment rate of 65%. This means two-thirds of customers who add items to their cart do not complete the purchase.
The Goal:
Reduce the cart abandonment rate by 45%.
The Approach:
To address this issue, Sierra Design will utilize the Root Cause Tree Technique. This visual method will help identify the underlying factors contributing to the high abandonment rate. By mapping out potential causes and their relationships, the company can gain valuable insights and develop effective solutions.
Solution
Step 1: Identify Possible Causal Factors
Problem | 65% Cart Abandonment Rate |
Causal Factors | Possible causal factors for high cart abandonment rates include:
|
Step 2: Identify the Root Cause
To identify the root causes of the 65% cart abandonment rate, utilize the previously identified causal factors to construct a Root Cause Tree.

Key Considerations for Effective Root Cause Tree Analysis
When implementing a Root Cause Tree Analysis, consider the following:
Incorporate Diverse Perspectives: Encourage input from stakeholders with varying backgrounds to ensure a comprehensive analysis.
Maintain Objectivity: Strive for objectivity and avoid making assumptions during the analysis.
Iterative Process: The Root Cause Tree analysis is an iterative process. Revise and refine the tree as new information becomes available.
Data-Driven Approach: Utilize data to support and validate the identified causes.
Identify Fundamental Causes: Pinpoint the most fundamental root causes at the deepest level of the tree.
Document and Share: Document the tree and share findings with relevant stakeholders.
Develop and Implement Solutions: Based on the identified root causes, develop and implement effective solutions.
Cross-Industry Applications of Root Cause Trees
Here's how Root Cause Trees are used across different roles:
Data Analysts can use Root Cause Trees to analyze data quality issues, investigate data anomalies, and identify errors in data systems.
Web Analysts can leverage Root Cause Trees to analyze website traffic decline, investigate low conversion rates, and analyze website performance issues.
Product Analysts can utilize Root Cause Trees to analyze product failures, investigate product delays, and analyze product adoption decline.
Security Analysts can employ Root Cause Trees to investigate security breaches, analyze IT system vulnerabilities, and analyze the origin of security incidents.
Conclusion
The Root Cause Tree Technique is a valuable tool for effectively identifying the underlying factors driving business challenges. By systematically analyzing potential causes and utilizing a visual framework, organizations can gain a deeper understanding of the root issues. By implementing the insights gained through Root Cause Tree analysis, businesses can develop targeted solutions, improve decision-making, and ultimately achieve their desired outcomes.
Data Analytics Training Resources
Analysts Builder
Master key analytics tools. Analysts Build provides in-depth training in SQL, Python, and Tableau, along with resources for career advancement. Use code ABNEW20OFF for 20% off. Details: https://www.analystbuilder.com/?via=amara









Comments